A dishonoured cheque, commonly referred to as a “bounced cheque,” occurs when a bank refuses to process a cheque due to various errors or insufficient funds. Understanding the causes, consequences, and prevention strategies can help in both personal and business financial management and avoid unnecessary legal or financial issues. 1 2 3 4
What Is Dishonour of Cheque?
A dishonoured cheque represents a breakdown in the payment process—it signals that the transaction for which the cheque was issued cannot be completed. The Indian banking system treats cheque dishonour seriously, with potential legal consequences under the Negotiable Instruments Act, 1881, including penalties or imprisonment for repeat offenders. 2 4
Major Causes of Cheque Dishonour
Banks may refuse to honour a cheque for several reasons. Here are the most frequent causes:
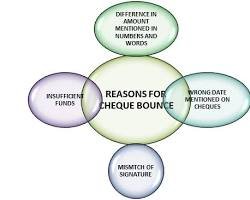
Insufficient Funds: This is the leading cause; the issuerʼs account doesnʼt have enough balance to cover the cheque amount.
Signature Mismatch: If the signature on the cheque does not match the specimen signature on record, banks reject it.
Overwriting or Material Alterations: Any changes made on the cheque must be properly attested by the drawer. Otherwise, it raises suspicion and leads to dishonour.
Mismatch in Amounts or Figures: When the amount mentioned in words does not tally with that in numbers, banks refuse to process the cheque.
Post–dated or Stale Cheques: Presenting a cheque before its due date (post-dated) or after its validity period (commonly six months, i.e., stale cheque) leads to dishonour.
Incorrect Date or Missing Details: Absence of key details such as a date, name of payee, or amount may result in rejection.
Account Closure: Issuing a cheque on a closed account will automatically result in a dishonour.
Stop Payment Instructions: If the drawer requests the bank to stop payment on a cheque, it is dishonoured.
Frozen or Inoperative Account: Legal actions, death, or insolvency of the drawer may freeze accounts, causing all issued cheques to bounce.
Damaged Cheque: Physical damage, tearing, or scribbling on cheques is yet another reason for dishonour.
Legal and Financial Consequences
Cheque dishonour can have wide-reaching impacts. In India, if the bank returns a cheque unpaid due to insufficient funds, the issuer can be prosecuted under Section 138 of the Negotiable Instruments Act. Penalties may include fines, payment of twice the cheque value, or even imprisonment for repeat offences. Additionally, banks typically charge a fee for each dishonoured cheque, which may vary across banks.
Steps to Prevent Cheque Dishonour
Taking a few precautions can help prevent cheque dishonour:
Always ensure sufficient account balance before issuing a cheque.
Double–check details—date, figures, words, and signature—to ensure accuracy.
Never overwrite or alter cheque details without countersigning.
Destroy unused cheques from closed accounts.
Keep cheque books safe to prevent damage.
Opting for digital payment modes further reduces the risk of such errors, adding layers of reliability and convenience.
Human Insight: Real-Life Impact
Cheque dishonour not only affects personal finances but can hamper business relationships and reputation. For individuals, facing extra charges and legal hassles is a major concern, while firms may lose client trust. An embarrassing experience for most, it also serves as a stark reminder to maintain clarity, transparency, and carefulness in every transaction.
Image Prompt Idea
To visually enhance this blog, here is an image prompt suitable for AI image generation:
Conclusion
Cheque dishonour is a preventable issue stemming from simple errors or oversight, but its consequences can be far-reaching. By following careful practices, individuals and businesses can safeguard themselves from financial loss and legal challenges, fostering smoother and more responsible banking habits.
⁂CAUSE OF DISHONOUR OF CHEQUE
A dishonoured cheque, commonly referred to as a “bounced cheque,” occurs when a bank refuses to process a cheque due to various errors or insufficient funds. Understanding the causes, consequences, and prevention strategies can help in both personal and business financial management and avoid unnecessary legal or financial issues. 1 2 3 4
What Is Dishonour of Cheque?
A dishonoured cheque represents a breakdown in the payment process—it signals that the transaction for which the cheque was issued cannot be completed. The Indian banking system treats cheque dishonour seriously, with potential legal consequences under the Negotiable Instruments Act, 1881, including penalties or imprisonment for repeat offenders. 2 4
Major Causes of Cheque Dishonour
Banks may refuse to honour a cheque for several reasons. Here are the most frequent causes:
Insufficient Funds: This is the leading cause; the issuerʼs account doesnʼt have enough balance to cover the cheque amount.
Signature Mismatch: If the signature on the cheque does not match the specimen signature on record, banks reject it.
Overwriting or Material Alterations: Any changes made on the cheque must be properly attested by the drawer. Otherwise, it raises suspicion and leads to dishonour.
Mismatch in Amounts or Figures: When the amount mentioned in words does not tally with that in numbers, banks refuse to process the cheque.
Post–dated or Stale Cheques: Presenting a cheque before its due date (post-dated) or after its validity period (commonly six months, i.e., stale cheque) leads to dishonour.
Incorrect Date or Missing Details: Absence of key details such as a date, name of payee, or amount may result in rejection.
Account Closure: Issuing a cheque on a closed account will automatically result in a dishonour.
Stop Payment Instructions: If the drawer requests the bank to stop payment on a cheque, it is dishonoured.
Frozen or Inoperative Account: Legal actions, death, or insolvency of the drawer may freeze accounts, causing all issued cheques to bounce.
Damaged Cheque: Physical damage, tearing, or scribbling on cheques is yet another reason for dishonour.
Legal and Financial Consequences
Cheque dishonour can have wide-reaching impacts. In India, if the bank returns a cheque unpaid due to insufficient funds, the issuer can be prosecuted under Section 138 of the Negotiable Instruments Act. Penalties may include fines, payment of twice the cheque value, or even imprisonment for repeat offences. Additionally, banks typically charge a fee for each dishonoured cheque, which may vary across banks.
Steps to Prevent Cheque Dishonour
Taking a few precautions can help prevent cheque dishonour:
Always ensure sufficient account balance before issuing a cheque.
Double–check details—date, figures, words, and signature—to ensure accuracy.
Never overwrite or alter cheque details without countersigning.
Destroy unused cheques from closed accounts.
Keep cheque books safe to prevent damage.
Opting for digital payment modes further reduces the risk of such errors, adding layers of reliability and convenience.
Human Insight: Real-Life Impact
Cheque dishonour not only affects personal finances but can hamper business relationships and reputation. For individuals, facing extra charges and legal hassles is a major concern, while firms may lose client trust. An embarrassing experience for most, it also serves as a stark reminder to maintain clarity, transparency, and carefulness in every transaction.
Image Prompt Idea
To visually enhance this blog, here is an image prompt suitable for AI image generation:
Conclusion
Cheque dishonour is a preventable issue stemming from simple errors or oversight, but its consequences can be far-reaching. By following careful practices, individuals and businesses can safeguard themselves from financial loss and legal challenges, fostering smoother and more responsible banking habits.
⁂CAUSE OF DISHONOUR OF CHEQUE
A dishonoured cheque, commonly referred to as a “bounced cheque,” occurs when a bank refuses to process a cheque due to various errors or insufficient funds. Understanding the causes, consequences, and prevention strategies can help in both personal and business financial management and avoid unnecessary legal or financial issues. 1 2 3 4
What Is Dishonour of Cheque?
A dishonoured cheque represents a breakdown in the payment process—it signals that the transaction for which the cheque was issued cannot be completed. The Indian banking system treats cheque dishonour seriously, with potential legal consequences under the Negotiable Instruments Act, 1881, including penalties or imprisonment for repeat offenders. 2 4
Major Causes of Cheque Dishonour
Banks may refuse to honour a cheque for several reasons. Here are the most frequent causes:
Insufficient Funds: This is the leading cause; the issuerʼs account doesnʼt have enough balance to cover the cheque amount.
Signature Mismatch: If the signature on the cheque does not match the specimen signature on record, banks reject it.
Overwriting or Material Alterations: Any changes made on the cheque must be properly attested by the drawer. Otherwise, it raises suspicion and leads to dishonour.
Mismatch in Amounts or Figures: When the amount mentioned in words does not tally with that in numbers, banks refuse to process the cheque.
Post–dated or Stale Cheques: Presenting a cheque before its due date (post-dated) or after its validity period (commonly six months, i.e., stale cheque) leads to dishonour.
Incorrect Date or Missing Details: Absence of key details such as a date, name of payee, or amount may result in rejection.
Account Closure: Issuing a cheque on a closed account will automatically result in a dishonour.
Stop Payment Instructions: If the drawer requests the bank to stop payment on a cheque, it is dishonoured.
Frozen or Inoperative Account: Legal actions, death, or insolvency of the drawer may freeze accounts, causing all issued cheques to bounce.
Damaged Cheque: Physical damage, tearing, or scribbling on cheques is yet another reason for dishonour.
Legal and Financial Consequences
Cheque dishonour can have wide-reaching impacts. In India, if the bank returns a cheque unpaid due to insufficient funds, the issuer can be prosecuted under Section 138 of the Negotiable Instruments Act. Penalties may include fines, payment of twice the cheque value, or even imprisonment for repeat offences. Additionally, banks typically charge a fee for each dishonoured cheque, which may vary across banks.
Steps to Prevent Cheque Dishonour
Taking a few precautions can help prevent cheque dishonour:
Always ensure sufficient account balance before issuing a cheque.
Double–check details—date, figures, words, and signature—to ensure accuracy.
Never overwrite or alter cheque details without countersigning.
Destroy unused cheques from closed accounts.
Keep cheque books safe to prevent damage.
Opting for digital payment modes further reduces the risk of such errors, adding layers of reliability and convenience.
Human Insight: Real-Life Impact
Cheque dishonour not only affects personal finances but can hamper business relationships and reputation. For individuals, facing extra charges and legal hassles is a major concern, while firms may lose client trust. An embarrassing experience for most, it also serves as a stark reminder to maintain clarity, transparency, and carefulness in every transaction.
Image Prompt Idea
To visually enhance this blog, here is an image prompt suitable for AI image generation:
Conclusion
Cheque dishonour is a preventable issue stemming from simple errors or oversight, but its consequences can be far-reaching. By following careful practices, individuals and businesses can safeguard themselves from financial loss and legal challenges, fostering smoother and more responsible banking habits.
⁂







